Cooperative Optimization Approaches for Distributing Service Points (Research Project)
 a joined research project from the Algorithms and Complexity Group, TU Wien, Austria, and Honda Research Institute, Germany
a joined research project from the Algorithms and Complexity Group, TU Wien, Austria, and Honda Research Institute, Germany
Project Team
Thomas Jatschka
Günther Raidl
Tobias Rodemann
Topic
For many business models an optimal distribution of service points in a customer community is needed. Examples are charging/battery swapping stations of electric vehicles, bicycle/car sharing stations, and repair stations. When planning such systems, estimating under which conditions which customer demand can be fulfilled is fundamental in order to design and evaluate possible solutions. To this end, demographic data is usually interlinked with geographic information, data on public transport, the street network, knowledge on manifold special locations etc. Usually, the whole process is challenging and error-prone. Customer demand information determined in such ways typically is vague, and not uncommonly a system built on such assumptions is not as effective as originally hoped for due to major deviations in reality.
To possibly improve this situation, we propose a cooperative optimization approach that incorporates potential users on a large scale and more tightly into the data acquisition as well as the optimization process. We confront the potential customers with certain location scenarios and ask them how these would suit his needs and how possibly these scenarios can be improved to fulfill more of his demand. This feedback is used to incrementally gain more knowledge about how much demand may be fulfilled under which conditions. New, more promising candidate location scenarios can then be derived and again be presented to the users. The process is iterated on a large scale with many potential users and many rounds until a satisfactory solution is reached.
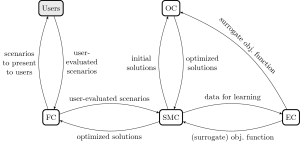
The figure below depicts the components of the framework of our cooperative optimization approach and their interaction. The general framework consists of the following components: an evaluation component (EC), an optimization component (OC), a feedback component (FC), and a solution management component (SMC).